Back to Blog
AI Technology
Can AI Chatbots Remember Past Conversations? Find Out
Find out how AI chatbots store, recall, and use past conversations to improve responses, plus key privacy considerations.
November 4, 2025
7 min read

In this blog, we explore a confusing AI topic: chatbot memory—their ability to recall previous conversations.
Do AI agents truly "remember" your history, or is each interaction a clean slate? We'll detail how chatbots handle memory, its impact on user experience, and the cutting-edge future where memory is smarter, more persistent, and secure.
The Basics of AI Chatbots and Memory: It Depends on the Design
AI chatbots "remember" conversations differently than humans. Unlike human memory, which is fluid and personal, Conversational AI systems rely on programmed rules, math, and structured data. Whether they can maintain a conversation's context across sessions hinges entirely on the engineering of their data persistence layer.
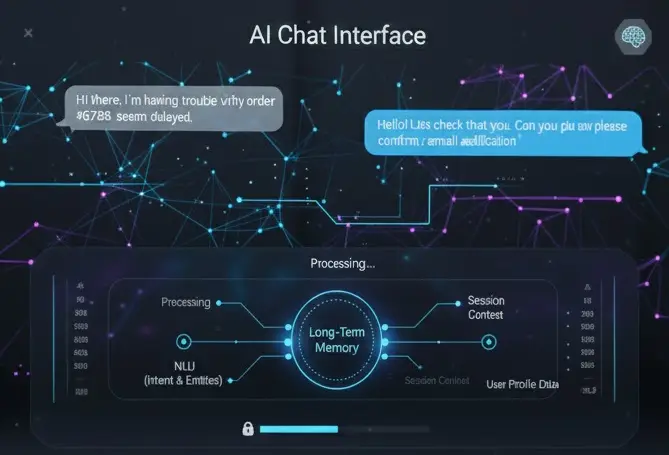
To clarify the debate, we must distinguish between two fundamental types of chatbot memory:
1. Session Memory (The Short-Term Buffer)
Most chatbots, especially those handling simple inquiries, rely on session memory. This means they remember what’s been said within the confines of a single, active conversation.
- Mechanism: The AI holds the conversation history in a temporary operational buffer, often related to the concept of context window in Large Language Models (LLMs). For example, if you tell a chatbot your name ("My name is Alex") or preferences early in a session, it can refer back to that information ("Hello, Alex") to make the interaction smoother.
- Duration: This kind of memory is short-lived. It typically disappears entirely once you close the chat window, clear your browser session, or if the interaction times out. It exists solely to manage the immediate, ongoing dialogue.
2. Long-Term Memory (The Persistent Profile)
Long-term memory, however, is a different beast entirely. This defines the capacity of advanced chatbots to recall past conversations over days, weeks, or even months.
- Mechanism: Chatbots achieve this permanence by storing chat transcripts, extracted user preferences, and synthesized profile data in external servers or structured databases linked specifically to a user's identity. The AI consults this database when a returning user initiates a new chat.
- Duration: This memory is persistent. If you’ve chatted before, the bot "remembers" previous topics, issues, or preferences, allowing for a far more personalised and human-like experience. This is crucial for building continuous customer relationships.
Book a Free Strategy Call
Talk to our automation experts about your specific challenges. We'll share proven strategies that have helped 500+ businesses save 40-70% on operations.
Book Free CallHow Do AI Chatbots Truly Remember Past Conversations?
Past conversation recall relies on a technical stack for storage and retrieval. Chatbot input is actively processed, vectorized, and stored, not just passively viewed.
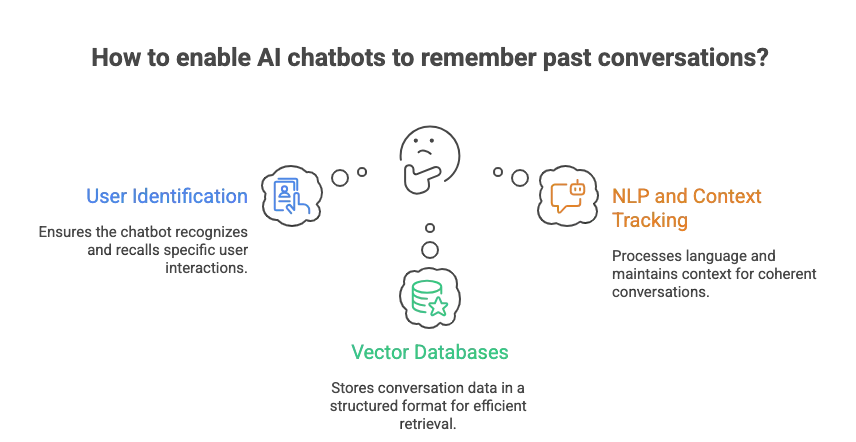
1. User Identification Is Key
The greatest technical challenge in long-term memory is connecting the dots between conversations. If you visit a chatbot anonymously and clear your browser cookies, the bot has no unique identifier. However, memory becomes possible when the user provides an identifiable hook:
- Explicit Log-in: Logging into a website account, providing an email, or entering an account number.
- Biometric/Device ID: For virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa), the system recognizes the user's voice profile or the registered device.
This identity allows the AI to pull up your complete historical chat profile, enabling that warm, personalized greeting: “Welcome back! I saw we chatted about your pending order last week.”
2. The Role of Vector Databases and Embeddings
Modern, sophisticated memory systems, especially those powering LLMs, do not just save plain text. They use a method known as Embeddings and Vector Databases:
- Embeddings: Your conversation history is converted into numerical representations (vectors) that capture the semantic meaning of the words, not just the words themselves.
- Vector Database: These vectors are stored in specialized databases that allow the AI to quickly search for semantic similarity. When you ask a new question, the AI retrieves not just exact keyword matches, but historical snippets that are conceptually related, even if the wording is different.
This advanced retrieval mechanism, often called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is what allows systems like ChatGPT to synthesize past conversation threads into a relevant new response, even when the conversation history is massive.
3. Natural Language Processing and Context Tracking
Memory isn’t just about storing data; it’s about making sense of it. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is essential for:
- Contextual Clues: The AI uses NLP to identify how previous talks established context. If you told the bot last time you needed help booking flights to "Paris" and this session you mention "my trip," the chatbot can link those details using the entity ("Paris") stored in your profile, offering tailored assistance without you repeating the destination.
- Token Management: In LLMs, session memory is heavily constrained by token limits (the maximum number of words/data the model can process at once). If a conversation gets too long, older parts must be summarized or discarded to make room for new input, illustrating a constant, internal struggle with memory management.
Limitations and The Critical Privacy Barrier
It’s important to highlight that chatbot memory, particularly the long-term variety, doesn’t come without significant caveats and constraints.
The Technical Pitfalls
On the technical side, limitations exist in how effectively chatbots actually retain and use memory:
- Context Decay: As conversations lengthen and old data is summarized or pushed out of the token window, subtle nuances or specific details can be lost, leading to "forgetfulness" or simple errors.
- The Clutter Problem: Remembering too much can sometimes trip up bots—taking older, now-irrelevant data into account and misinterpreting the present context. Designers must strike a crucial balance between helpful recall and clutter-free, efficient conversations.
- Computational Cost: Retrieving and processing massive amounts of historical data from a vector database is computationally expensive, often adding milliseconds of latency to every single AI response.
The Privacy and Ethical Imperative
Data storage fundamentally means data risks. Privacy is a massive consideration, especially when conversations might include sensitive information (financial details, health symptoms, personal opinions).
- Transparency and Consent: Companies are under legal and ethical pressure (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) to be transparent about what conversation data they save, how they secure it, and for how long. Ensuring users' explicit consent to store and utilize their sensitive data is not just good practice, but a legal necessity.
- Responsible Use: The integrity of the AI depends on using conversations responsibly. Data must be anonymized or aggregated for model training, and never linked back to individuals, identifying information for unauthorized use.
Why Does Memory Matter for the User Experience?
Memory gives chatbots a decisive edge, transforming them from simple tools into valuable digital companions.
- Reduced Friction and Repetition: When your support bot can remember your previous ticket number, past transaction details, or ongoing issue, it eliminates the user's frustrating need to "repeat my story," speeding up resolution times and dramatically improving satisfaction.
- Deep Personalization: Memory enables tailored experiences. Imagine a bot that remembers your specific dietary restrictions from last week's order and automatically filters restaurant suggestions, or suggests relevant products based on the exact specifications you previously browsed. This kind of nuanced, proactive service builds crucial customer loyalty.
- Building Empathy: For specialized services like therapeutic or mental health bots, memory is non-negotiable. The AI’s ability to recall your mood logs, previous struggles, and past coping mechanisms is vital for offering better, context-aware, and emotionally validating ongoing support
The Future of Chatbot Memory: Smarter, More Sensitive, and Secure
Looking ahead, we can expect significant advances in how AI chatbots handle conversation memory, pushing persistence beyond the limits of current hardware and token windows.
1. External, Permanent Context Retention
Emerging technologies are exploring context retention that spans indefinite periods. This involves combining multi-modal inputs—meaning chatbots will recall not just what you said, but related images, calendars, documents, or location data you’ve shared, integrating them all into a holistic "user state."
2. On-Device and Decentralized Processing
To address privacy and cost, innovations like Federated Learning and on-device data processing are becoming mainstream. The AI model itself might be trained centrally, but the actual memory retrieval and personalization processing happen locally on your device. This gives users far more control over what their digital helpers remember and ensures that sensitive data never leaves their secure personal device.
3. Emotionally Intelligent Memory
The frontier of Emotional AI is directly linked to memory. Future systems will recall not just what you said, but how you felt when you said it. If a user previously expressed extreme frustration over a service, the AI will recall that emotional state and approach the current conversation with greater caution and pre-programmed empathy (adjusting the NLG tone) before even attempting to solve the technical problem.
Wrapping Up: Do AI Chatbots Really Remember You?
Can AI chatbots remember past conversations?
Yes, but their "memory" is technical—a mix of session data, token management, and structured records linked to your identity—not human-like. It's limited by design, privacy laws, and data quality.
As a user, appreciate the progress while being mindful of what you share. Engineering a more responsive AI requires thoughtfully designing its ability to "remember" you—a blend of technology and the human need for personalized connection.
Book a Free Strategy Call
Talk to our automation experts about your specific challenges. We'll share proven strategies that have helped 500+ businesses save 40-70% on operations.
Book Free Call
About Divyesh Savaliya
Divyesh leads Flowlyn with 12+ years of experience designing AI-driven automation systems for global teams.


