Back to Blog
AI Technology
How Conversational AI Works? (With Examples)
This guide completely explains how Conversational AI works with live examples and important pointers you must know before investing.
November 1, 2025
8 min read

In an increasingly digital world, the way businesses interact with their customers is undergoing a profound transformation. Gone are the days of endless waiting times. Enter Conversational AI, a technology that allows machines to understand, process, and respond to human language in a way that feels natural and intuitive.
In this guide learn how conversational AI works, exploring its mechanics, benefits, challenges, and what the future holds for this transformative technology.
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI is a set of technologies that enable computers to simulate human conversations through voice or text.
It encompasses various fields, including natural language processing, machine learning, and deep learning, to allow machines to understand context, intent, and sentiment. The goal is to make human-computer interaction as seamless and effective as human-to-human interaction, below is an example of it.
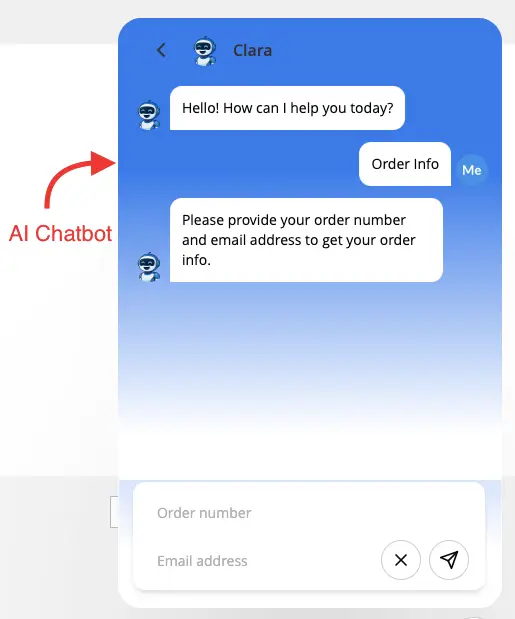
Types of Conversational AI Technologies
Conversational AI isn't a single technology but a spectrum of tools designed for different interaction styles:
- Chatbots: These AI chatbots improve customer experience with their typically text-based interfaces designed to simulate human conversation. They can range from rule-based bots that follow predefined scripts to AI-powered bots that use NLP to understand and respond to complex queries.
- Virtual Assistants: Often voice-enabled (like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant), these are more sophisticated than chatbots. They can understand commands, answer questions, perform tasks (like setting reminders or playing music), and often integrate with multiple services.
- Voicebots/IVR Systems: These use voice recognition and synthesis to interact with users over the phone. Modern voicebots powered by AI can understand natural speech, significantly improving the experience compared to traditional touch-tone IVR systems.
- Intelligent Virtual Agents (IVAs): These are advanced virtual assistants capable of handling more complex, personalized, and proactive interactions, often leveraging deep learning for nuanced understanding and response generation.
How Conversational AI Works?
The magic behind conversational AI lies in several interconnected technological components. Here are the core components of Conversational AI.
| Component | Role in the Process | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
NLP | The Translator | Understands intent and extracts specific entities from raw text. |
ML/Deep Learning | The Engine | Learn from training data to improve accuracy and detect sentiment. |
Dialogue Manager | The Brain | Decides the logical next step based on context and business rules. |
NLG | The Voice | Converts structured data back into natural, human-like language. |
These four core technical stages that transform raw human input into a meaningful digital response.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This is the foundational layer. NLP acts as the "translator" between human speech and computer logic. It performs three critical tasks:
- Understanding Input: It converts human language (text or speech) into a structured format the machine can process.
- Identifying Intent: It determines what the user actually wants to achieve, such as "checking a bank balance" or "scheduling a meeting."
- Extracting Entities: It pulls out specific data points, like dates, locations, or product names (e.g., "tomorrow at 3 PM").
2. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning
These technologies provide the AI with the ability to "learn" from past interactions rather than just following rigid rules.
- Training Data: By analyzing millions of past conversations, the AI learns common phrases and patterns.
- Context Management: Advanced AI maintains "state," meaning it remembers what was said earlier in the chat so it doesn't ask the same question twice.
- Sentiment Analysis: The system detects the emotional tone—such as frustration or joy—and adjusts its response accordingly.
3. Dialogue Management
Think of this as the "brain" of the operation. Once the intent is known, the Dialogue Manager decides the most logical next step. It weighs the user's input against the current context and business rules to determine if it should provide an answer, ask a clarifying question, or hand the conversation over to a human agent.
4. Natural Language Generation (NLG)
Finally, the AI must respond. NLG is the process of turning the machine’s internal decision back into human-like text or speech. This ensures the output isn't just a string of data, but a grammatically correct, helpful sentence that feels natural to the user.
Benefits of Conversational AI in 2026
The advantages of deploying conversational AI are far-reaching, impacting customer experience, operational efficiency, and revenue:
- 24/7 Availability: AI agents never sleep. They provide instant support and information around the clock, improving customer satisfaction and lead capture.
- Instant Responses: Customers don't have to wait in queues. Queries are addressed immediately, leading to quicker resolutions and happier users.
- Improved Customer Experience: By providing personalized and efficient interactions, conversational AI enhances satisfaction and builds stronger customer relationships.
- Cost Reduction: Automating routine inquiries and tasks significantly reduces the workload on human agents, leading to lower operational costs.
- Scalability: AI can handle an unlimited number of simultaneous conversations, making it easy to scale customer support without adding headcount.
- Data Collection & Insights: Every interaction provides valuable data about customer behavior, preferences, and pain points, which can inform business strategy.
- Lead Generation & Qualification: AI can engage website visitors, answer questions, and pre-qualify leads before handing them off to sales, boosting efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations of Conversational AI
One of the most significant challenges is the struggle to interpret nuance, as AI often fails to grasp complex human emotions, sarcasm, irony, or highly ambiguous language.
While rule-based bots are strictly confined to their scripts, even sophisticated AI can falter when encountering inquiries that fall outside of its specific training domain. This can lead to a "depersonalized" user experience if the system lacks a seamless handover process to a human agent, potentially alienating customers who require a more empathetic or specialized touch.
The structural implementation of AI presents its own set of obstacles, particularly regarding integration complexity and data security. Connecting conversational tools with existing CRMs, databases, and enterprise systems is often a technical challenge that requires precise configuration.
Simultaneously, businesses must maintain robust security measures and adhere to strict privacy regulations to protect sensitive customer information. To stay effective, these systems require continuous training and monitoring to adapt to evolving linguistic patterns, product updates, and shifting user expectations, ensuring the AI remains a reliable asset rather than a liability.
Conversational AI Best Practices
Define Clear Objectives
Avoid deploying AI simply for the sake of following a trend. Instead, start with a specific business problem you want to solve—such as "reducing password reset calls by 30%" or "decreasing initial lead response time to under 60 seconds." Having a concrete goal allows you to measure success accurately and tailor the AI's logic to meet that specific need.
Start Simple, Then Expand
The most successful AI implementations follow a phased approach. Begin by automating high-volume, low-complexity tasks like FAQs or basic order tracking. As you gather real-world interaction data and insights, you can gradually expand the AI’s capabilities to handle more nuanced workflows and complex troubleshooting.
Design for Seamless Handover
No AI can solve every problem. To prevent user frustration, ensure there is a clear and immediate path for users to escalate the conversation to a human agent. A "seamless handover" includes passing the chat transcript to the live representative so the customer doesn't have to repeat their issue, maintaining a high standard of service.
Personalize When Possible
To make interactions feel less robotic, leverage your existing customer data. By integrating the AI with your backend systems, the bot can greet users by name, reference their recent orders, or provide tailored recommendations. This level of personalization builds rapport and increases engagement rates.
Monitor and Iterate
Conversational AI is not a "set it and forget it" tool. You should regularly review conversation logs, analyze user feedback, and track key performance metrics. Use these insights to identify where the AI is failing or where users are dropping off, and use that data to retrain and refine your models continuously.
Integrate with Existing Systems
For a unified and effective experience, your conversational AI should not operate in a silo. Connect it directly to your CRM (like HubSpot or Salesforce), your internal knowledge base, and your inventory management tools. This allows the AI to provide real-time, accurate information and update customer records automatically.
Maintain Transparency
Honesty is crucial for user trust. Be upfront with users by clearly stating they are interacting with an AI assistant. This sets appropriate expectations for the conversation and often makes users more patient with the technology's limitations.
Examples of Conversational AI in Action
To understand the versatility of this technology, it helps to see how specific sectors have moved away from manual forms and phone queues in favor of intelligent, real-time dialogue.
E-commerce & Retail
- Uses AI for: Handling "Where is my order?" (WISMO) queries, processing returns, providing product recommendations based on browsing history, and managing cart abandonment through proactive reminders.
- Benefit: Dramatically reduces the volume of repetitive support tickets, allowing the team to focus on complex cases while increasing conversion rates through personalized shopping assistance.
Banking & Financial Services
- Uses AI for: Real-time balance inquiries, fund transfers between accounts, bill payments, and guiding customers through the initial stages of loan or credit card applications.
- Benefit: Provides customers with instant, secure access to financial services 24/7 without the need for a human teller or navigating complex phone menus.
Healthcare
- Uses AI for: Symptom triaging and assessment, automated appointment scheduling, providing medication reminders, and offering verified information on common medical conditions.
- Benefit: Improves patient access to care and ensures clinic staff are not bogged down by administrative scheduling, leading to a more efficient triage process.
Marketing & Sales
- Uses AI for: 24/7 lead qualification, booking sales demos, delivering personalized lead magnets, and scoring prospects based on their interactions.
- Benefit: Ensures that "speed to lead" is optimized, capturing high-intent prospects the moment they express interest.
Human Resources (HR)
- Uses AI for: Answering internal policy questions, guiding new hires through onboarding documentation, and managing employee leave or vacation requests.
- Benefit: Frees up HR professionals from answering the same repetitive questions, allowing them to focus on employee culture and high-level talent development.
Travel & Hospitality
- Uses AI for: Finding and booking flights or hotels, providing real-time updates on gate changes or flight delays, and managing simple re-bookings or cancellations.
- Benefit: Enhances the traveler experience by providing frictionless, real-time updates during high-stress situations without forcing the user to wait on a support line.
What’s Next for Conversational AI?
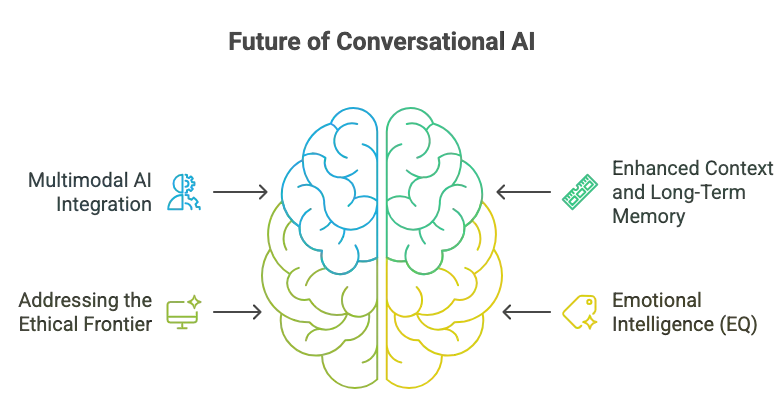
1. Multimodal AI Integration
The future is beyond text and voice. Multimodal AI leverage on AI voice agents, text, images, and even real-time video or gestures into the conversation.
Scenario: Picture an assistant that not only listens to you but also sees your surroundings through your smartphone camera. If you say, "Help me fix this," it could identify the broken gadget, pull up the correct repair manual, and provide step-by-step guidance annotated directly over the live video feed.
2. Enhanced Context and Long-Term Memory
Current systems often struggle to maintain context across days or weeks. Future CAI will feature significantly improved long-term memory architectures, allowing them to remember preferences, past purchases, emotional states, and complex project details indefinitely, making every interaction highly personalized.
3. Addressing the Ethical Frontier
As AI becomes more powerful, addressing ethical concerns is paramount:
The Models must be continuously checked and refined to remove harmful biases inherited from training data, ensuring fair and equitable interactions for all users.
For critical applications, AI needs to move beyond generating plausible text to ensuring factual accuracy. Techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which ground responses in verified, external data sources, will become standard to curb the tendency of LLMs to "hallucinate" false information.
4. Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
The next evolution moves from pure linguistic intelligence to Emotional AI. This involves systems that can detect subtle emotional cues (e.g., hesitation, frustration in tone, or aggressive word choice) and adjust their response (NLG) to display appropriate empathy or compassion. This is especially vital for mental health, elder care, and sensitive customer service applications.
Book a Free Strategy Call
Talk to our automation experts about your specific challenges. We'll share proven strategies that have helped 500+ businesses save 40-70% on operations.
Book Free CallThe Bottom Line
Conversational AI is redefining how we communicate with machines, bridging gaps between complex technology and natural human interaction. It’s a sophisticated blend of NLP, Deep Learning, and continuous data training that powers tools ranging from the helpful to the delightfully creative.
By understanding the intricate loop between NLU, Dialogue Management, and NLG, we gain appreciation for why these tools are becoming so pervasive.
Conversational AI is not just a passing trend; it is a fundamental shift in user interface design. Whether you’re a tech expert or just someone who loves the convenience of chatting with your smart assistant, there’s no denying that CAI is a crucial part of our digital future—and it’s only getting more exciting.

About Divyesh Savaliya
Divyesh leads Flowlyn with 12+ years of experience designing AI-driven automation systems for global teams.


